The pymraid principle notes
Chapter 8 - Define the Problem
Problems usually arise when you have an undesired result -R1, but you want a desired outcome - R2. The solution is the steps taken from R1 to R2.
Technically, the method to define the problem is called continuous analysis and follows the following questions:
- Is there/is it possible to have a problem (or opportunity)?
- Where is the problem?
- why does it exist (the root cause of the problem)?
- What can we do?
- How do we do it? Where Q1 and Q2 define the problem, and Q3-5 is the best approach to finding the optimal solution.
Key elements and structure
Normally, the problem indicating the gap between the undesired result and the desired outcome is caused by a certain situation or under a set of conditions. The problem could be displayed clearly with key elements including:
- Starting Point/Open Scene
- Disturbing Event
- Current Situation - R1, Undesired Result
- End Goal - R2, Desired Result
Starting Point
Make short assumptions or descriptions to lay out the situation.
Disturbing Event
The disturbing event is something happening now/ about to happen/will happen, and it poses a challenge or threat to the existing situation that is relatively stable. It includes:
- External Causes: changes that occurred outside the current structure or environment, e.g. new competitor, new technology, government policy, consumer policy changes, etc
- Internal causes: changes that occurred within the organization, e.g. new SOP, technology adoption, entering a new market, product line adjustment, etc.
- other reasons: evidence shows possible changes, e.g. lack of product performance, lower than average operational standard, and reports showing a shift in customer behavior, etc.
Current Situation, R1
R1 indicates the problem that the client is trying to solve or an opportunity that the client is trying to catch, it could be more than one and it is recommended to show as a simple description in the sketch. e.g. decreasing market share, revenue decreasing, profit loss or missing market opportunity, etc.
End Goal, R2
R2 is the expected outcome, give a specific or quantitative description is helpful to judge whether the end goal is achieved or not. e.g. achieving annual revenue growth by 25% more, adjusting on operational system for greater production, etc.
Example of Sketches
As the reader follows left to right to bottom structure, there are several possible questions be posed, it could be categorized into following 7 scenarios:
Chapter 9 - Structurly Analyzes the Problem
The standard procedure of analyzing a problem follows gathering information - describe finding - arrive conclusion - provide solution, however, this process brings a lot of unnecessary informations gathered. Hence, a new approach has been developed:
- Purpose assumption
- Design experiment to eliminate assumptions
- Arrive conclusion via experiments
- Provide relevant solutions
In another words, this is pushing yourself to think of the root cause of the problems, this requires you to really study the structure of the industry you are working on.
Design the framework
Framework is designed to help you to make assumption for client’s problem, this kind of assumption will eventually indicate the factor or activity you are suppose to focus on. There are 3 known methods: Present shape structure, Finding reason and problem, Classification.
Present Shape Structure
Any firm or industry should have a clear structure, including multiple unit for a system and each have a specific cause. Outlining the structure is helpful for understanding the process and the trend of the industry.
Finding reason and problem
This is to find the corresponding factor, action, or task of the problem, mainly used in financial structure, task sructure, and action structure.
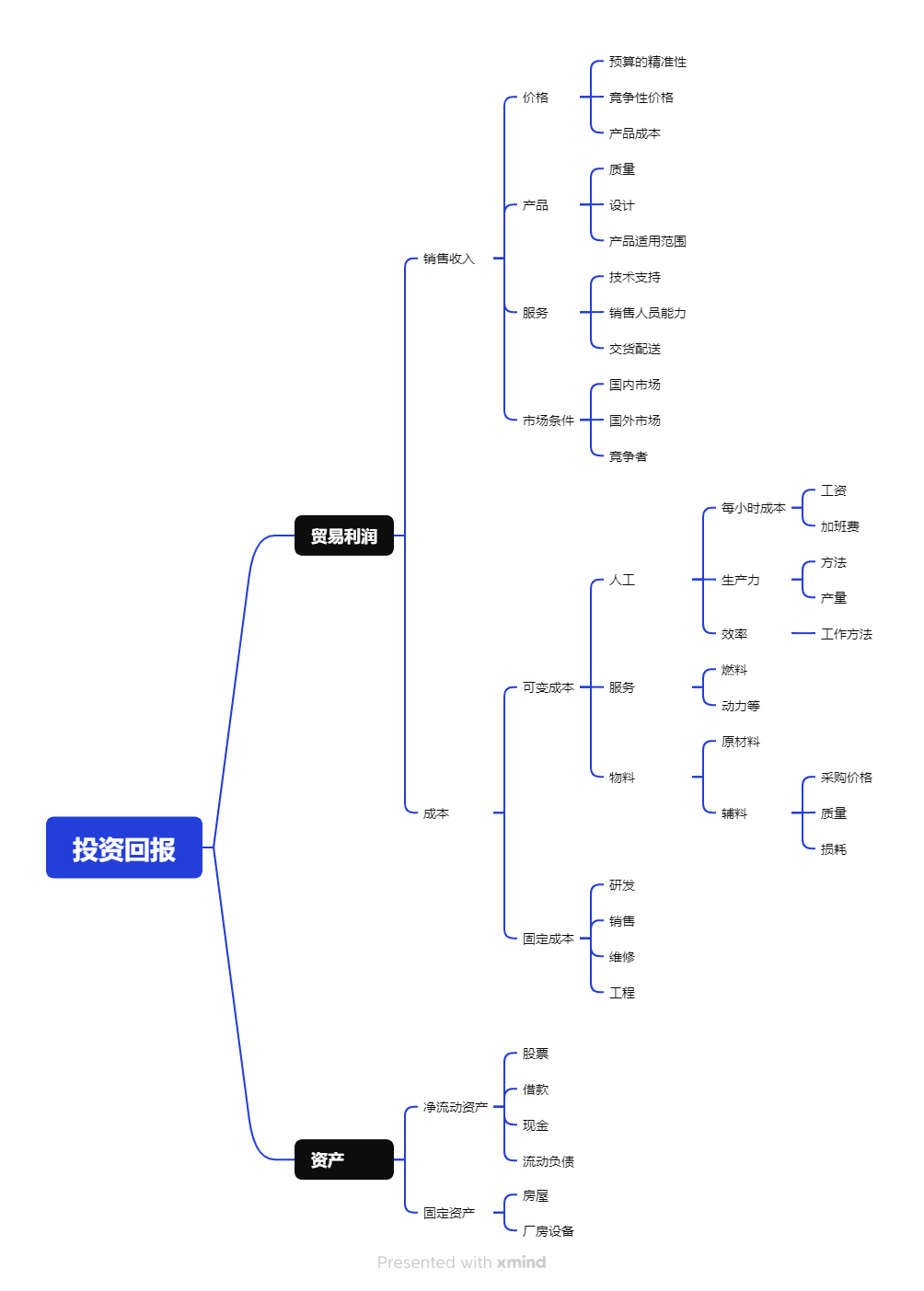
The finacial structure is set to quickly define where the problem factor is and provide the solution.
The task structure is designed to lay out the tasks to ahcieve the goal, for example, if we want to improve the revenue, we can either increase the no. of sales or increase the unit price.
The action structure is listing out the problem first and break down into actions, key point is to use a tree diagram to find the optimal solution to solve an undesired outcome.
Classification
Here we use MECE principle for each layer and set up the binary question to help us to determine the problem solution. Alternatively, we can use a decesion tree approach to rule out the undesired outcome, with binary quesitons set up for each node.
Applying the framework
The solution is depends on how much you know about the industry, in terms of manufacture, sales, system, etc. The framework to solve the problem is usually hidden within the starting point/situation of the problem defining process.
The most effective way to arrive a conclusion is to deceide the framework first and only gather the required information to validate the assumption.
Building logic tree
Answer the following first:
- Is there a problem?
- where is the problem?
- why does it exist?
- what can we do?
- how do we do?
Using a logic tree allow us to find the solution logically and provide MECE solution.
Issue analysis
Sometime it’s called issue analysis which is not an accurate term to address, originally, the word “issue” is from the legal term “at issue”, meaning two parties debate on one topic until win. Therefore, only use issue for a binary question, other question could addressed as concern.
The key for issue analysis is to draw the flowchart of the situation with rank, indicating the main bariable decision - MVD for each phase,including the environmental, economical, and social factors for each activity. Then, make assumption for those MVD and based on the impact of each MVD to make decision. Note the binary question or the issue is not the question from the client, but a situation that casued R1(Undesired outcome).